LMO Act
Background
- A variety of LMO have been developed and used with advances in biotechnology, and international efforts have been made to prevent related risks to human health and the environment,
- As a result, the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety (CPB) was adopted in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) held in Montreal, Canada, in January 2000, which took effect in September 2003 across the world.
- Korea, in preparation for ratification of CPB, enacted and proclaimed the Transboundary Movement, Etc. of Living Modified Organisms Act (LMO Act) in March 2001. After the ratification of CPB in October 2007, the LMO Act took effect on January 1, 2008.
History of LMO Act
- 2000. 09. signed the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety (CPB)
- 2001. 03. enacted the Transboundary Movement, Etc. of Living Modified Organisms Act (LMO Act)
- 2005. 09. established the Enforcement Decree of the LMO Act
- 2006. 03. established the Enforcement Rule of the LMO Act
- 2007. 10. ratified CPB
- 2007. 12. established the Consolidated Public Notification on Transboundary Movement, Etc. of Living Modified Organisms
- 2008. 01. enforced the LMO Act
- 2008. 02. revised the LMO Act and the Enforcement Decree
- 2008. 03. revised the LMO Act and the Enforcement Decree
- 2008. 12. revised the LMO Act and the Enforcement Decree
- 2009. 02. revised the LMO Act and the Enforcement Decree
- 2013. 12. revised the LMO Act
- 2014. 07. revised the Consolidated Public Notification
- 2015. 06. revised the Consolidated Public Notification
Purpose
The LMO Act prescribes matters required for the enforcement of the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety and for securing safety
related to the development, production, import, export, distribution, etc. of LMO with the aim of preventing risks caused by
LMO to the public health and preservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in advance and promoting the lives of the people
and international cooperation. (LMO Act - Article 1)
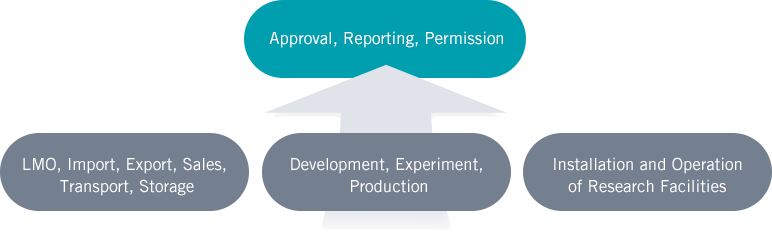
Subjects of LMO Act
- Persons who intend to import, export, transport, sell and store LMO
- Persons who intend to develop, experiment and produce LMO
- Persons who intend to install and operate LMO research facilities
※ LMO that is used for medicines for the human body is not subject to the Act.
National Biosafety Management System
According to the LMO Act, several government agencies assume respective roles depending on the use of LMO. The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy takes charge of overall affairs as the responsible state agency, and the Biosafety Committee is responsible for the enforcement of the Protocol, safety management planning, etc.
- Biosafety Committee - a national review organization with the Prime Minister serving as the director
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs - acting as an international channel for matters related to biosafety
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy - the responsible state agency in charge of overall affairs
- Korea Biosafety Clearing House - in charge of collecting and managing domestic and overseas information to support review
works of related government agencies - Related departments of central administrative agencies - serving respective roles depending on characteristics of LMO
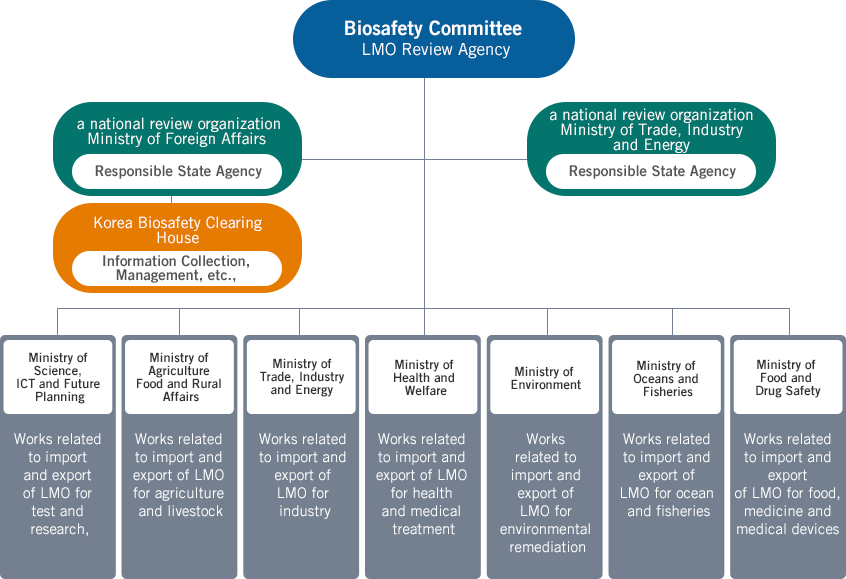
Note : 'Works related to import and export' refers to the works related to the development, production, export, sales, transport,
storage, etc. of LMO